UML-期末复习
Published:
UML期末复习笔记
UML
概述
背景
软件危机 software crisis
- projects running over-budget
- projects running over-time
- software was very inefficient
- software was of low quality
- software often did not meet requirements
- projects were unmanageable and code is difficult to maintain
solution to software crisis
software complexity is inherent
reduce and control the complexity of software
basic method of controlling software complexity
- divide
- abstract
- modularization 模块化
- information hiding
软件生命周期 software life cycle
UML 在软件生命周期的每个阶段均有应用
requirement analysis 需求分析
use case diagram
software design 软件设计
class diagram
interaction diagram
state machine diagram
activity diagram
coding/programming 实现
class diagram
testing/debug 测试
class diagram
component diagram
deployment diagram
running/maintenance 运行维护
deployment diagram
软件过程模型 software process model
瀑布模型 waterfall model
线性、顺序模型
易于理解与使用
每个过程都有详细、具体的可交付代码以及反馈
对于小型、需求易于理解的项目比较友好
但缺乏灵活性
不能适应变化的需求
原型模型 prototype model
步骤
- 确认基本需求
- 开发初步原型
- 反馈回顾原型
- 重构、拓展原型
特点
- 循环
- 引入客户评价
- 时时改进、修改
与客户关系紧密
增量模型 incremental model
模块化,不断加入总的工程中
螺旋模型 spiral model
增量模型加入风险评估
- 每个螺旋拥有四个过程
- planning
- risk analysis
- engineering
- evaluation
软件工程方法及技术
structured method
重视数据流
优点
易于掌控
方法更为成熟,有更多支持的工具
缺点
开发效率低,复用性差
object-oriented method
系统由对象构成
对象间通信
对象既包含数据又包含行为
对象被分为类,各个类之间建立继承关系
UML对面向对象支持比较好
object and instance-对象和实例
class-类
encapsulation-封装
inheritance-继承
polymorphism-多态
message passing-通信
RUP rational unified process
六个最佳方案
- develop iteratively迭代式开发
- manage requirements 需求管理
- use components 组件化
- model visually 模型可视化
- verify quality
- control changes
core workflow工作流
core process workflows
- business modeling 商业建模
- requirements 需求
- analysis & design 分析与设计
- implementation 实现
- test 测试
- deployment 部署
core supporting workflows
- configuration & change management 配置 & 变化管理
- project management 项目管理
- environment 环境
four phases
- inception
- elaboration
- construction
- transition
RUP 4+1 view model
- logical view
- development view
- physical view
- process view
- +1——scenarios
UML Unified Modeling Language
basic building block基本构造块
- thing 事物
- structural things
- class
- interface
- collaboration
- use case
- active class
- component
- artifact & node
- behavioral things
- interaction
- state machine
- activity
- grouping things
- package
- annotational things
- note
- structural things
- relationship 关系
- dependency
- association
- generalization
- realization
- diagram 图
- structural diagrams
- class diagram
- component diagram
- object diagram
- deployment diagram
- package diagram
- composite structure diagram
- profile diagram
- behavior diagram
- activity diagram
- use case diagram
- state machine diagram
- interaction diagram
- sequence diagram
- communication diagram
- interaction overview diagram
- timing diagram
- structural diagrams
rule 规则
- name
- scope
- visibility
- integrity
- execution
common mechanism
- specification
- adornment
- common division
- extensibility mechanism
- stereotypes
- tagged values
- constraints
Use case modeling 用例建模
requirements technology
two types of requirements
- functional requirements
- non-functional requirements
three types of requirements technology
user story in extreme programming(XP)
as a
, I want so that feature description in feature-driven development(FDD)
the <by|for|of|to> a(n) use case in rational unified process(RUP)
use case is the basic characteristics
use case driven software development process
use case model
use case diagram
analysis model
class diagram, package diagram
design model
class diagram, package diagram, object diagram, component diagram
deployment model
component diagram, deployment diagram
test model
use case
definition
use cases are a means to capture(采集、捕捉) the requirements of systems.
A use case is a specification(规范、规格) of behavior
use cases define interactions between external actors and the system to attain particular goals
name
every use case must have a name that distinguishes it from other use cases
a name is a textual string(文本字符串)
in practice, use case names are short active verb phrases naming some behavior found in the vocabulary of the system you are modeling
elements of use case diagram
use case
actor
a human, a hardware device, even another system plays with a system
actors之间可以有泛化关系
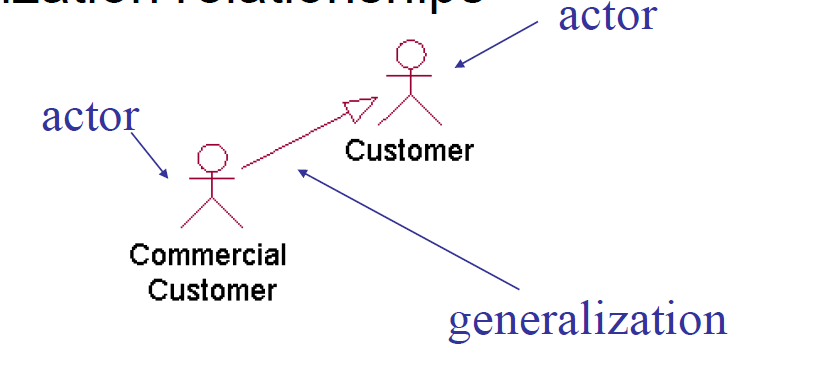
relationship
参与者之间为泛化关系
参与者与用例为关联关系
用例之间有泛化关系、include、extend(后两种为依赖关系的特殊形式)
included 用例不能单独存在(虚线+线箭头,指向被include)
extended 用例可以单独存在(虚线+线箭头,指向base)
class diagram
class definition
一类具有相同的属性、方法、关系、语义的对象的集合的描述。
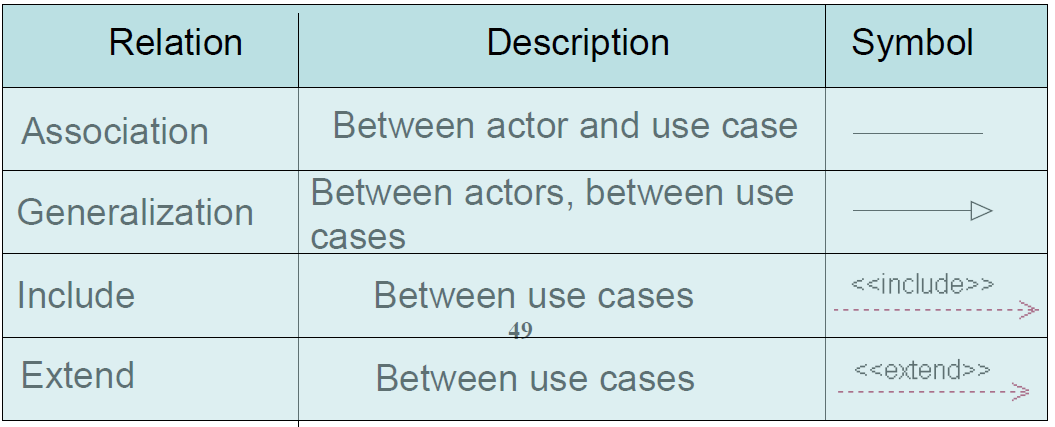
relationships 关系
斜体表示抽象类
依赖
泛化
聚合
组合
关联
实现

three stereotypes of class
- boundary class
- entity class
- control class
three perspectives of class diagram
- conceptual 概念层
- specification 说明层
- implementation 实现层
principles of object oriented class design
open closed principle(OCP)开闭原则
对扩展开放,对修改关闭
在需求变化时,可以在不修改源代码或者二进制代码的前提下,扩展模块的功能,使其满足新的需求
liskov substitution principle(LSP)里氏替换原则
继承必须保证父类的性质不被改变
子类可以扩展父类原有的功能,但不能改变父类原有的功能
如:几维鸟不会飞,故不能继承自会飞的鸟类
dependency inversion principle(DIP)依赖倒置原则
高层模块不应该依赖底层模块,两者都应该依赖其抽象,抽象不应该依赖细节,细节应该依赖抽象。
核心思想:要面向接口编程,不要面向实现编程。
interface segregation principle(ISP)接口分离原则
一个类对另一个类的依赖应该建立在最小的接口上
activity diagram 活动图
constituent elements of activity diagram
- initial node
- final node
- activity node
- control flow
- decision node and guard expression
- merge node
- fork node and join node
state machine diagram 状态机图
concept of the state
a state of an object is a period of time during which it satisfies some condition, performs some activity, or waits for some event
- name
- entry/exit effects
- internal transitions
- substates
- deferred events
constituent elements of state machine diagram
- initial state and final state
- transition
- source and target state
- event trigger
- guard condition
- effect
object diagram&package diagram 对象图&包图
representation of objects
- a name is a textual string
包为分组事物
owned elements in package diagram
- classes
- interfaces
- components
- nodes
- collaborations
- use cases
- diagrams
- even other packages
relationships between package
dependency
«import»
code——using, import
«access»
能访问另一个包中的信息,但命名空间没有合并
«trace»
包的发展历史
generalization
principles of package design
the release reuse equivalency principle(REP)重用发布等价原则
重用粒度就是发布粒度。一个包中的类要么都是可以重用的,要么就都不可以重用。
the common reuse principle(CRP)共同重用原则
一个包中的所有类应是共同重用的
the common closure principle(CCP)共同封闭原则
一个变化如果对一个包中的类产生影响,则对整个包中的所有类产生影响,对其他包中的类不产生影响
the acyclic dependencies principle(ADP)无环依赖原则
包间的依赖关系不允许存在环
interaction diagram 交互图
sequence diagram 顺序图
constituent elements of sequence diagram
- object
- lifeline
- focus of control
- message
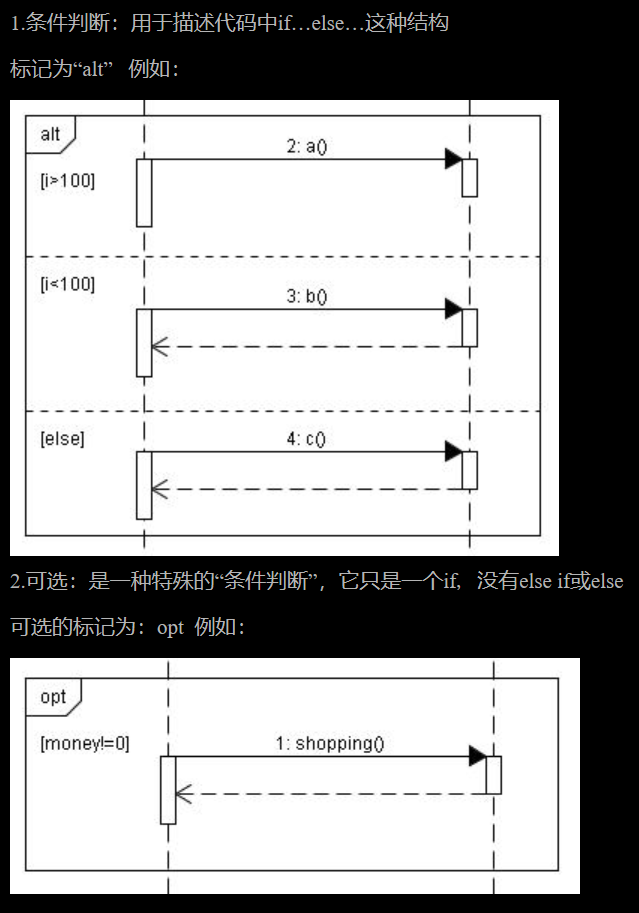
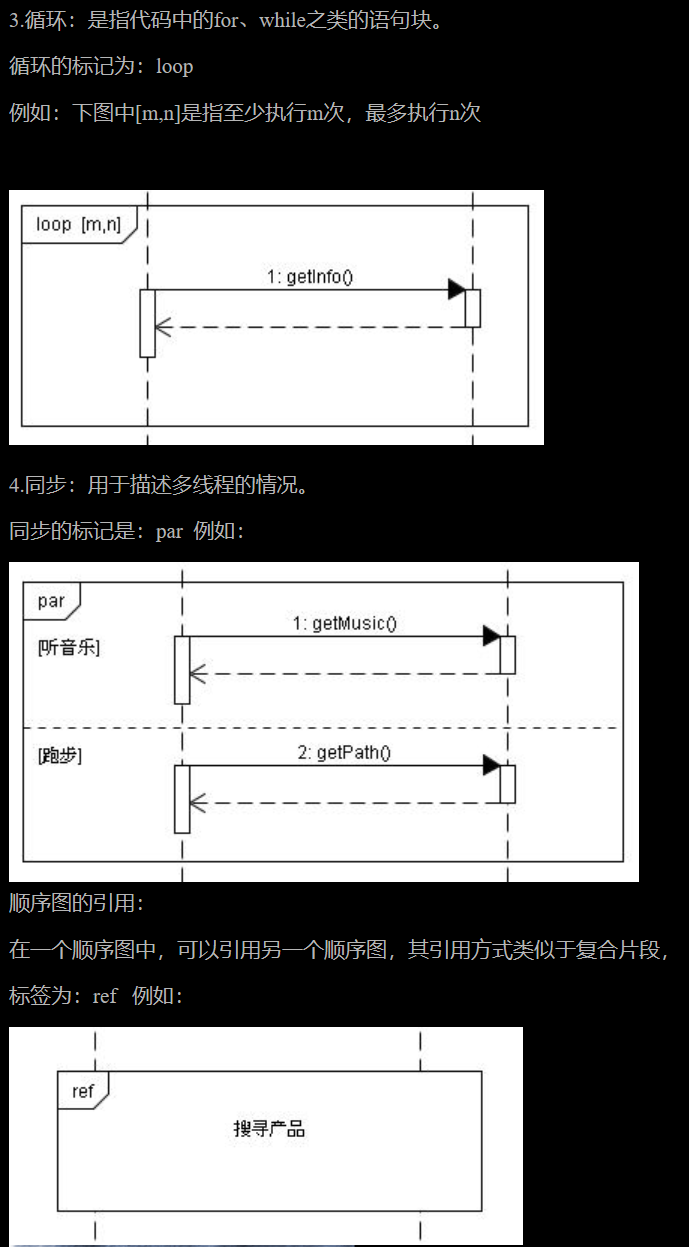
communication diagram 通讯图
constituent elements of communication diagram
- object
- link
- message
comparison between sequence and communication diagram
顺序图强调消息传递的时间顺序,通讯图强调参加一个交互的对象的组织结构
因为均来自于UML的元模型的同一信息,所以他们在语义上是等价的
timing diagram(强调时间特性)
interaction overview diagram(顺序图+活动图)
component diagram构件图
展现构件间的组织结构、依赖关系
强调系统的静态实现、运行
比类图更抽象
deployment diagram部署图
forward and reverse engineering
forward engineering
图–>代码
reverse engineering
代码–>图
